Documentation
Solution Architecture
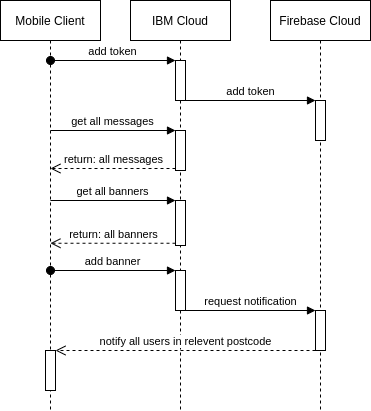
The solution has a simple architecture, requiring mobile clients to connect to an IBM hosted cloud retrieve data when necessary and the IBM cloud to use a Firebase Messaging Service to send notifications. The following architecture diagram depicts this relationship:
App Design
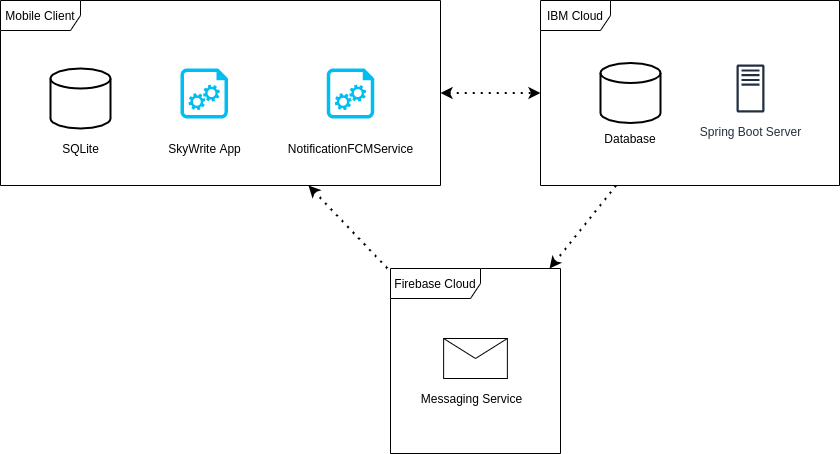
The app consists of 4 fragments that represent different screens within the app. Each fragment class has an associated class that inherits from the ViewModel. The ViewModel class is built into the Android SDK and is responsible for storing and displaying UI-related data. The HomeFragment is the screen where the AR messages can be viewed, therefore, it must implement the SampleRender.Renderer interface. The SampleRender.Renderer interface comes from the AR Core library and, when implemented, allows AR messages to be displayed using the phone’s camera.
The diagram below shows the relationships between the classes. For brevity, some of the classes do not contain attributes as there are too many to display.
Database Design
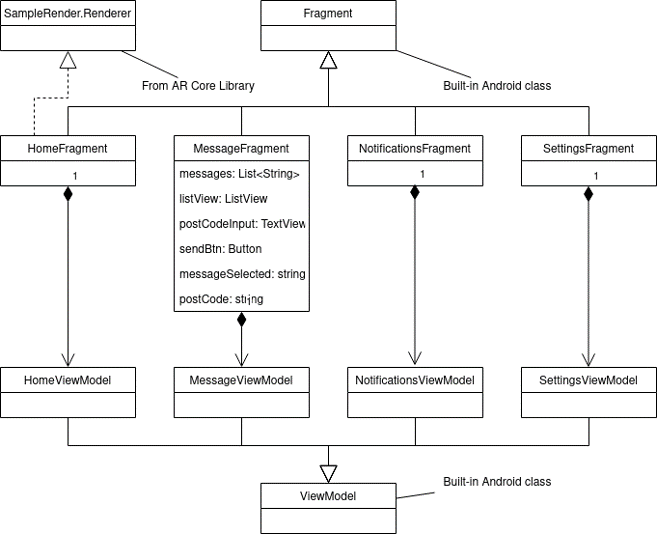
A database is required to store data about messages and banners. Messages contain an id, a message to be displayed when sent, and an object file name which is where the data for 3D model is stored. Each banner represents a message which has been sent to a specific postcode. A banner contains a postcode, a messageId, and a timestamp of when it was created. Below is a diagram that shows the relationship between banners and messages. Additionally, tokens are used to keep track of user’s devices which is used by the Firebase Messaging Service to direct notifications.
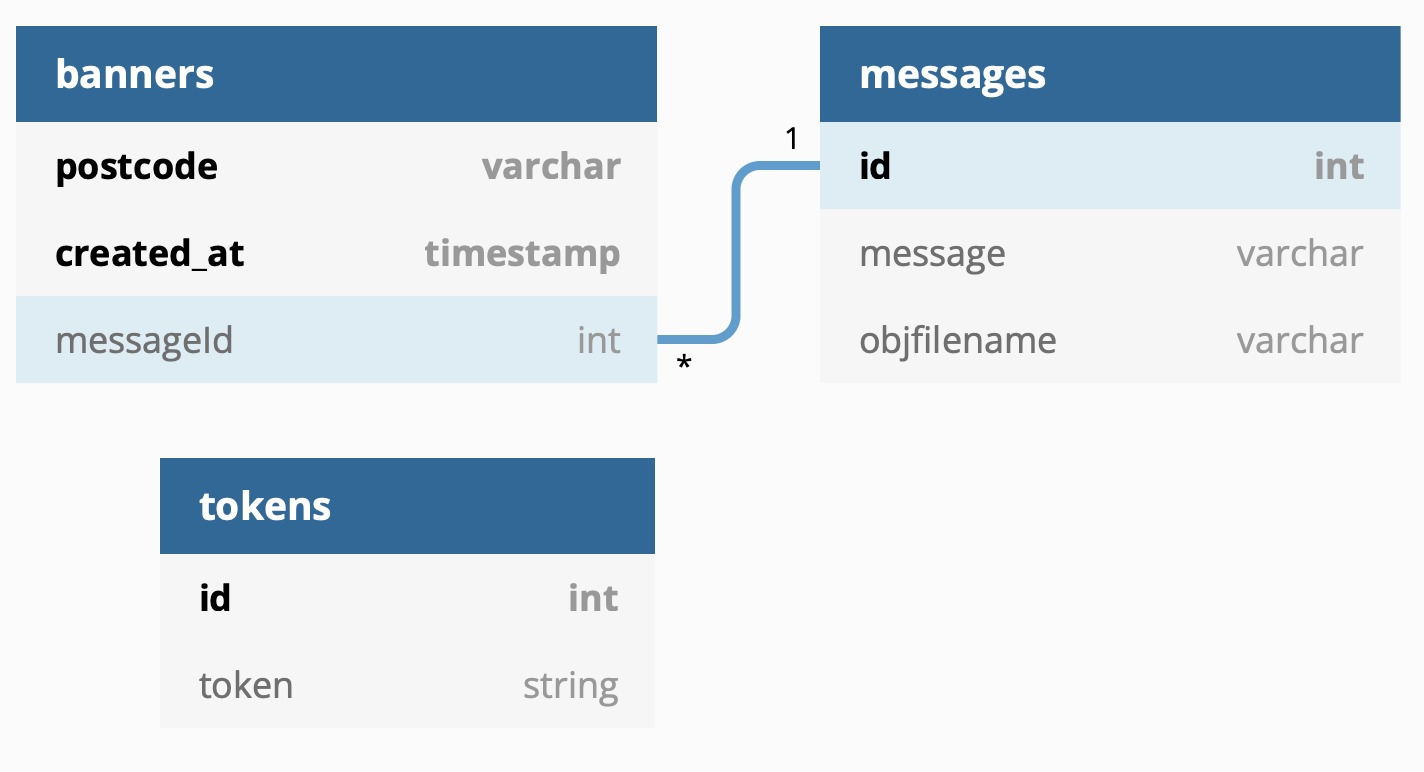
Below is a sequence diagram of an example interaction between the mobile client, the IBM database and server and the Firebase messaging service.